Using Jupyter Notebook as GIS
Contents
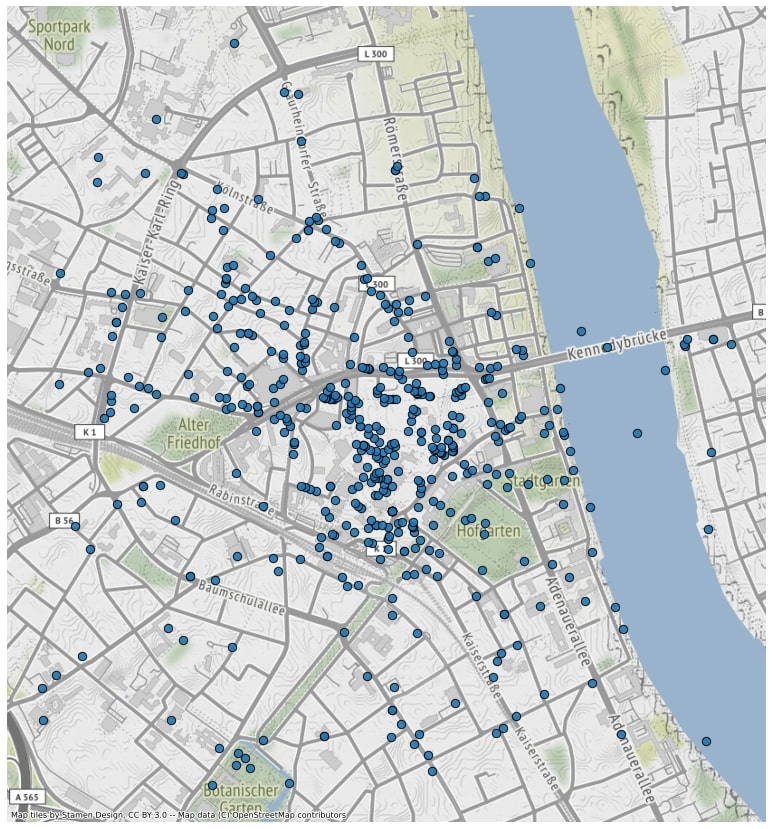
 Clipping a geodataframe and displaying it on a basemap in Jupyter.
Clipping a geodataframe and displaying it on a basemap in Jupyter.
Loading a geodataframe
Let’s load some points from a geojson file, i.e. from our preprocessed geodataframe mined with Fast Instagram Scraper:
| |
Clipping a geodataframe with another…
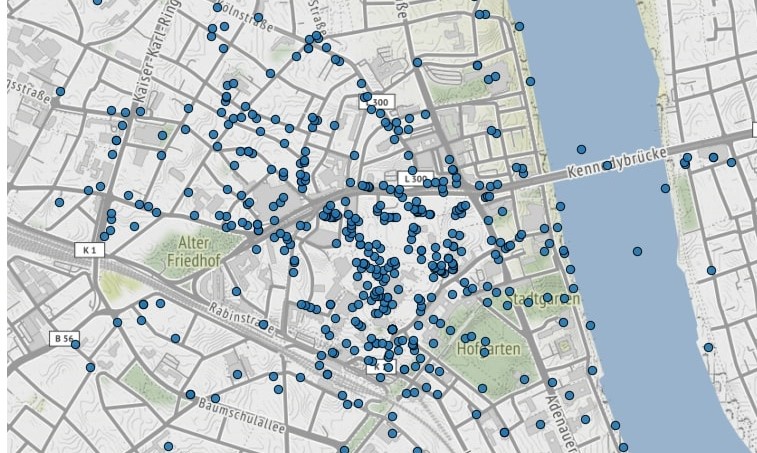
If we would like to clip these points to the extent of a city, geopandas.clip method is pretty straightforward. Note that geopandas can read a file directly from URL as well! Here we load a geojson file of the extent of Bonn.
| |
… or clipping by indexing coordinates
In case you don’t have an exact shape to clip for geodataframe, but want to quickly remove outliers, you can make use of geopandas.cx function. You can index coordinates and set a max or min latitude or longitude. First indexer is latitude, second longitude:
| |
Plotting points on a basemap
| |
The result will look like this: